Winmtr
Содержание:
What is MTR?
MTR is a network diagnostic tool which combines the results of both the ping and traceroute tools. When a computer connects to another computer over the internet, the network traffic is sent through a series of routers, or “hops”, in between the source and destination to efficiently deliver content. MTR looks at each of these hops and measures the latency and packet loss against each one, including the destination. This information allows us to figure out where a network problem lies.
For ExaVault, an MTR trace lets us see the network traffic between your system and the server hosting your files. This can help us pinpoint spots in the route where traffic is slowing down or getting lost.
Типы файлов MTR
Ассоциация основного файла MTR
.MTR
| Формат файла: | .mtr |
| Тип файла: | RealFight Radio Control File |
Файл MTR хранит данные радио управления, используемое RealFight тренажера, программное обеспечение моделирования управления моделями самолетов для Microsoft Windows.
| Создатель: | Knife Edge Software |
| Категория файла: | Файлы игр |
| Ключ реестра: | HKEY_CLASSES_ROOT\.mtr |
Программные обеспечения, открывающие RealFight Radio Control File:
RealFlight, разработчик — Knife Edge Software
Совместимый с:
| Windows |
Ассоциации других файлов MTR
.MTR
| Формат файла: | .mtr |
| Тип файла: | Id Tech 4 Material Defintions |
Файл MTR содержит определение материалов и справочные таблицы материала для ид Tech 4 игрового двигатель видео, разработанный для Doom 3. видеоигры.
| Создатель: | id Software |
| Категория файла: | Файлы игр |
Программы, открывающие файлы Id Tech 4 Material Defintions :
Doom, разработчик — id Software
Совместимый с:
| Windows |
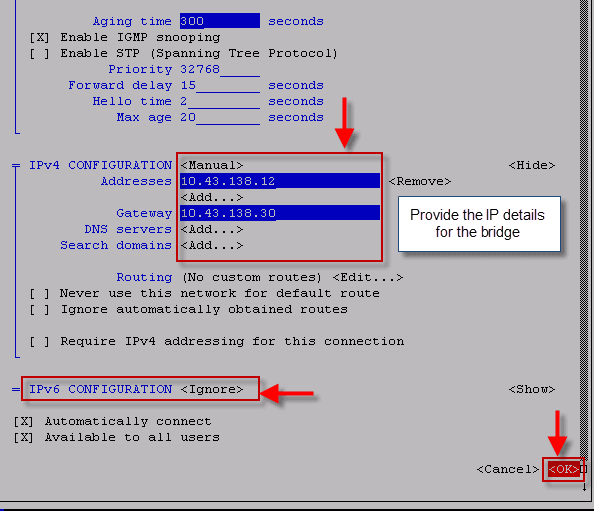
Understand MTR Report
Beyond providing the information about the path between the source and destination, MTR provides valuable statistics regarding durability of the connection.
- Lost% – Shows the % of packets loss at each hop.
- Snt – Shows the no:of:packets being sent.
- Last – Latency of the last packet being sent.
- Avg – Average latency of all packets.
- Best – Displays the best Round Trip Time for a packet to this host (shortest RTT).
- Wrst – Displays the worst Round Trip Time for a packet to this host (longest RTT).
- StDev – Provides the standard deviation of the latencies to each host.
Even if the “Avg” looks good, take a look at standard deviation. If the Standard deviation is high, then it may indicate that “Avg” is skewed by some measurement error or too much fluctuation. In such a case, take a look at Best and Wrst latency to make sure the average is good.
Fundamentals
MTR is licensed under the terms of the GNU General Public License (GPL) and works under modern Unix-like operating systems. It normally works under the text console, but it also has an optional GTK+-based graphical user interface (GUI).
MTR relies on Internet Control Message Protocol (ICMP) Time Exceeded (type 11, code 0) packets coming back from routers, or ICMP Echo Reply packets when the packets have hit their destination host. MTR also has a User Datagram Protocol (UDP) mode (invoked with «-u» on the command line or pressing the «u» key in the curses interface) that sends UDP packets, with the time to live (TTL) field in the IP header increasing by one for each probe sent, toward the destination host. When the UDP mode is used, MTR relies on ICMP port unreachable packets (type 3, code 3) when the destination is reached.
MTR also supports IPv6 and works in a similar manner but instead relies on ICMPv6 messages.
The tool is often used for network troubleshooting. By showing a list of routers traversed, and the average round-trip time as well as packet loss to each router, it allows users to identify links between two given routers responsible for certain fractions of the overall latency or packet loss through the network. This can help identify network overuse problems.
Beispiele
Die folgenden Beispiele zeigen einige mtr Abfragen. Die ersten drei Hops wurden dabei jeweils anonymisiert.
Interaktive Ausgabe
Die folgende Ausgabe zeigt den Aufruf von mtr. Unter Debian/Ubuntu ist der Parameter -t für die Konsolenversion erforderlich wenn das Paket mtr installiert ist (und nicht mtr-tiny):
mtr www.google.com
My traceroute
tpw (0.0.0.0) Wed Dec 18 09:24:14 2013
Keys: Help Display mode Restart statistics Order of fields quit
Packets Pings
Host Loss% Snt Last Avg Best Wrst StDev
1. dsldevice.lan 0.0% 24 68.4 66.2 4.8 100.6 23.8
2. XXXXX(Provider)XXXXX.at 0.0% 24 19.8 20.6 19.1 29.6 2.5
3. 195.3.66.157 0.0% 24 19.7 21.2 19.0 51.4 6.7
4. 195.3.68.1 0.0% 24 22.3 25.5 21.8 42.3 6.3
5. 195.3.70.154 0.0% 24 22.3 25.6 22.0 51.1 8.3
6. 62.47.120.150 0.0% 24 26.3 27.4 26.1 38.6 2.9
7. 209.85.243.119 0.0% 24 26.9 26.8 26.3 27.5 0.3
8. 209.85.241.212 0.0% 24 64.1 49.5 38.6 73.8 14.0
9. 209.85.251.249 0.0% 24 38.4 39.8 38.0 47.1 2.2
10. 209.85.242.49 0.0% 24 39.5 39.0 38.4 39.6 0.3
11. fra02s17-in-f20.1e100.net 0.0% 24 39.0 38.6 38.1 39.1 0.3
Report Ausgabe
mtr kann auch in einem Report-Modus () ausgeführt werden. Die Anzahl der Abfragen wird mit dem Parameter angegeben. Mittels erreicht man, dass lange Hostnamen vollständig anzeigt und nicht abgeschnitten werden:
user@tpw:~$ mtr -r -w -c 10 www.google.com HOST: tpw Loss% Snt Last Avg Best Wrst StDev 1.|-- dsldevice.lan 0.0% 10 96.9 42.2 1.3 99.8 47.3 2.|-- XXXXX(Provider)XXXXX.at 0.0% 10 19.9 20.7 19.4 28.3 2.7 3.|-- 195.3.66.157 0.0% 10 19.6 19.4 18.9 20.1 0.3 4.|-- 195.3.68.1 0.0% 10 21.9 22.3 21.9 22.7 0.2 5.|-- 195.3.70.186 0.0% 10 22.5 29.8 22.2 87.5 20.4 6.|-- 62.47.120.150 10.0% 10 46.2 34.3 26.3 76.8 17.2 7.|-- 209.85.243.119 0.0% 10 26.7 27.3 26.4 33.0 2.0 8.|-- 209.85.241.212 0.0% 10 51.9 54.6 40.1 61.6 6.1 9.|-- 209.85.251.249 0.0% 10 38.9 38.8 38.7 39.0 0.1 10.|-- 209.85.242.49 0.0% 10 39.7 39.3 38.8 40.2 0.4 11.|-- fra02s17-in-f18.1e100.net 0.0% 10 39.0 38.6 38.2 39.0 0.2 user@tpw:~$
Grafische Ausgabe
Die grafische Version wird mit dem Kommando xmtr gestartet bzw. bei Debian/Ubuntu mit mtr:
xmtr www.google.com
Das Kommando xmtr (mtr unter Debian/Ubunt) startet von der Kommandozeile aus die grafische Variante von mtr (My traceroute)
Резюме файла MTR
Расширение файла MTR имеет два тип (-ов) файла (-ов) и связано с два различными программными обеспечениями, но главным образом с RealFlight, разработанным Knife Edge Software. Часто они представлены в формате RealFight Radio Control File.
Основную часть этих фацлов классифицируют, как Game Files.
Файлы MTR можно просматривать с помощью операционной системы Windows. Они обычно находятся на настольных компьютерах (и ряде мобильных устройств) и позволяют просматривать и иногда редактировать эти файлы.
Рейтинг популярности файлов MTR составляет «Низкий», что означает, что данные файлы встречаются редко.
Advanced MTR techniques
Newer versions of MTR are now capable of running in TCP mode on a specified TCP port, compared to the default use of the ICMP (ping) protocol. However, in most cases this mode shouldn’t be used as TCP reports can be misleading in diagnosing inter-route issues. A TCP MTR will use SYN packets in place of ICMP pings, and most internet-level routers will not respond to these, erroneously indicating loss.
What a TCP test is useful for is determining whether firewall rules on a router somewhere are blocking a protocol or port, perhaps because port forwarding has not been configured properly. Running a TCP test over a certain port could more clearly reveal this whereas an ICMP test may not.
Running MTR in TCP mode will require super-user privileges on most machines:
Binary distributions
Ryan’s build and/or mirror apparenltly stopped working somewhere in 1999,
14 years ago and nobody noticed. Apparently not worth maintaining.
kanedaaa has packages up to slackware 12.1, also a while ago. Possibly
because mtr is included in the distribution.
The debian distribution has mtr builtin, so it would be preferrable to
just use that.
The freebsd ports link still works and has a reasonably recent version.
-
Ryan Weaver has been making RPMs for mtr. He puts them
on his ftp site, which I mirror ontoftp://ftp.bitwizard.nl/mtr/rpms/ .
- kanedaaa builds slackware packages at:
http://kaneda.bohater.net/slackware/packages/.
- The freeBSD team makes binaries at
ftp://ftp.FreeBSD.org/pub/FreeBSD/ports/i386/packages-stable/net/
Substitute the correct packages-..-current if you are running a «-current»
version. If anybody can tell me how I can get mirror to flatten the symlinks
that they use, I’ll mirror them here at BitWizard. -
The debian team makes binaries at
ftp://ftp.debian.org/debian/dists/unstable/main/binary-i386/net/mtr_0.39-1.deb
The mirror worked in 30 seconds, no problems there. So you can get the package
from the BitWizard site
too. -
Michael Collard no longer builds and maintains x64_64 binaries at:
http://members.iinet.net.au/~quadfour/projects.html. (the link is dead. I don’t
expect Michael to still do this, If he does and you know the new location, tell me.)
If you want to contribute binaries in a way similar to this, feel
free to volunteer.
Analyse
user@tpw:~$ mtr -r -w -c 10 www.areca.com.tw
HOST: tpw Loss% Snt Last Avg Best Wrst StDev
1.|-- dsldevice.lan 0.0% 10 42.9 63.0 42.7 97.5 21.8
2.|-- 194-166-175-254.adsl.highway.telekom.at 0.0% 10 19.5 20.8 19.4 28.9 3.0
3.|-- 195.3.66.157 0.0% 10 18.7 19.3 18.5 19.8 0.4
4.|-- 195.3.68.1 0.0% 10 21.9 27.1 21.7 70.7 15.3
5.|-- 195.3.70.178 10.0% 10 22.5 25.4 21.8 39.3 6.3
6.|-- win-b4-link.telia.net 0.0% 10 22.7 22.7 22.4 23.0 0.2
7.|-- prag-bb1-link.telia.net 0.0% 10 28.9 28.7 28.4 29.2 0.3
8.|-- ffm-bb1-link.telia.net 0.0% 10 99.3 56.1 46.7 99.3 18.9
9.|-- ash-bb3-link.telia.net 30.0% 10 142.3 149.8 136.7 193.0 19.5
| `|-- 213.155.131.145
| |-- 213.155.135.61
| |-- 80.91.250.203
| |-- 213.155.135.57
10.|-- sjo-bb1-link.telia.net 80.0% 10 215.8 212.9 210.0 215.8 4.1
| `|-- 213.155.135.129
11.|-- chunghwa-ic-155505-sjo-bb1.c.telia.net 80.0% 10 204.6 208.6 204.6 212.7 5.7
12.|-- r4001-s2.tp.hinet.net 50.0% 10 346.3 345.5 343.3 346.4 1.3
13.|-- 220-128-12-2.HINET-IP.hinet.net 90.0% 10 341.3 341.3 341.3 341.3 0.0
14.|-- tpdt-3011.hinet.net 90.0% 10 346.4 346.4 346.4 346.4 0.0
15.|-- TCHN-3011.hinet.net 80.0% 10 357.6 358.1 357.6 358.5 0.6
16.|-- ??? 100.0 10 0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0
user@tpw:~$
Bei dieser Abfrage geht es offensichtlich zwischen folgenden Routern über eine längere Seekabelverbindung durch ein Meer, erkennbar an den hohen Differenzen der durchschnittlichen Pingzeiten (Avg):
- zwischen Hop 8 (56.1 ms) und 9 (149.8 ms)
- zwischen Hop 11 (208.6 ms) und 12 (345.5 ms)