Your network
Содержание:
- USB LAN-Dongle
- Previous Minor Release: Version 14.2 Highlights
- Miscellaneous options
- Untangle
- logfile options
- Настройка
- Roadwarrior connection (Host-to-Net)
- Конфигурация
- VyOS
- Introduction
- System Details
- Меню IPFire
- Setting up the Blue Network
- Shell tools
- Version 15.1 Highlights
- Security
- Advanced Settings and Cipher Selection
- pfSense
- #7 IPCop (https://distrowatch.com/)
- #4 ClearOS (https://www.clearos.com/)
- LAN Cards/Onboard Chips
- #8 ufw (https://help.ubuntu.com/community/UFW)
- NG Firewall Apps
- IPFire
USB LAN-Dongle
| LAN-Card name | Type | ID | Loaded Modules/Drivers | tested with Core | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ADMtek | |||||
| AN8515 Pegasus II | 100 MBit/s / USB2.0 | 07a6:8515 | pegasus | 100 | |
| Apple | |||||
| USB Ethernet Adapter A1277 | 100 MBit/s / USB2.0 | 05ac:1402 | asix | 139 | re-branded AX88772 |
| ASIX | |||||
| ASIX Electronics Corp. AX88178 | 1000 MBit/s / USB2.0 | 0b95:1780 | asix | 142 | |
| ASIX Electronics Corp. AX88179 | 1000 MBit/s / USB3.0 | 0b95:1790 | ax88179_178a | 139 | very low current |
| ASIX Electronics Corp. AX88772 | 100 MBit/s / USB2.0 | 0b95:7729 | asix | 100 | |
| ASIX Electronics Corp. AX88772 | 100 MBit/s / USB2.0 | 0b95:772a | asix | 138 | 250 mA max |
| D-Link Corp. | |||||
| D-Link DUB-E100 HWVer.: B1 (Fast Ethernet USB 2.0 Adapter) | 100 MBit/s / USB2.0 | 2001:3c05 | asix | 67 | |
| Delock | |||||
| Delock 62121 (AX88179) | 1000 MBit/s / USB3.0 | 0b95:1790 | asix | 100 | |
| Kronton | |||||
| DM9601 Fast Ethernet adapter | 100 MBit/s / USB2.0 | 0b95:772b | dm9601 | 141 | from DX.com |
| Logilink | |||||
| UA0144 10/100 Mbps Ethernet adapter | 100 MBit/s / USB2.0 | 0b95:772b | asix | 72 | |
| MosChip Semiconductor | |||||
| MCS7830 10/100 Mbps Ethernet adapter | 100 MBit/s / USB2.0 | 9710:7830 | mcs7830 | 100 | |
| Netgear | |||||
| FA120 100Mbit Ethernet adapter | 100 MBit/s / USB2.0 | 0846:1040 | asix | 72 | |
| RealTek Semiconductor Corp | |||||
| RTL8153 Gigabit Ethernet Adapter | 1000 MBit/s / USB3.0 | 0bda:8153 | RTL 8153 | 142 | 200 mA max |
| SMSC | |||||
| ` | Standard Microsystems Corp. 2202 Ethernet | 100 MBit/s / USB1.1 | 0707:0200 | pegasus | 142 |
| SMSC 9512 USB2.0LAN + USB HUB | 100 MBit/s / USB2.0 | 0424:9512 | smsc95xx | 66 | |
| Trendnet | |||||
| TU3-ETG USB 3.0 to Gigabit Ethernet adapter | 1000 MBit/s / USB3.0 | 0b95:1790 | asix ax88179_178a | 125 |
Previous Minor Release: Version 14.2 Highlights
Untangle NG Firewall 14.2 includes significant enhancements to web security and content filtering, the ability to synchronize users with Azure Active Directory, and enhancements to intrusion detection and prevention.
Visibility and Control for Educational and other Content-sensitive Environments
These capabilities provide network administrators in content-sensitive environments such as schools, libraries or social services to meet compliance requirements while safeguarding users.
- Web Filter enables administrators to flag, block or alert based on search words on Google, YouTube, Ask, Bing, and Yahoo.
- Enforcement of safe search for YouTube; YouTube usage can be locked down to show only content that meets the ‘safe search’ criteria.
- Logging of YouTube searches performed on the network.
- Enhanced malware detection with an even greater percentage of the internet categorized to block more attacks originating from web browsing.
Directory Connector: Azure Active Directory
Directory Connector has been updated to allow users to connect via Azure Active Directory. For those customers using Office365, they can now utilize their existing directory service with accounts, groups and policies already established. This saves customers time during deployment, general maintenance of user groups and policies, and when provisioning or off-boarding users.
Intrusion Prevention: Better Performance & Easier Customization
- Intrusion Rule ID is now visible so IT admins can see which rule was responsible for a log/block action in reports.
- UI performance updates for better user experience and faster load times.
Additional Enhancements
- Ability to hide the network name of the wireless access point. This provides increased security from hackers and devices looking to join networks with malicious intentions.
- Ability to set the time for Configuration Backup to be performed.
For a full list of changes in NG Firewall 14.2, please see the changelog.
Important Technical Notes on Upgrade
Untangle NG Firewall version 14.2 and above implements URL categorization powered by Webroot Brightcloud. This replaces the same functionality provided by Zvelo in prior versions. You can find answers to common questions related to the upgrade in this article. By October 30, 2019, customers will need to have upgraded to at least 14.2.0 in order for categorization of web pages to work.
Pricing & Availability
Untangle NG Firewall version 14.2 is available as a free download. Current Untangle customers will be able to upgrade seamlessly at no charge.
Miscellaneous options

- Client-to-Client — This option makes it possible that the OpenVPN clients can communicate with each other. By the usage of different subnets, the above mentioned «Route Push Options» should be used to make the different subnets accessible for each other.
- Redirect-Gateway def1 — Directs all IP traffic through the VPN client (e.g. web browser).
-
LZO-Compression compresses the data passing through the tunnel. Thus network traffic is reduced, but CPU utilization is increased.
Note: comp-lzo should be disabled since it could make the tunnel attackable under specific circumstances via the so called Voracle attack.
-
Additional configuration — Delivers the possibility to extend the server but also the client configuration with individual directives. If you activate it by setting the hook, two more configuration files named server.conf.local and client.conf.local, which are located under the path /var/ipfire/ovpn/scripts will be read out and written under the original server.conf and/or the respective client.ovpn.
- This feature was delivered with Core 89.
- Since this feature was a community development, you can find some examples of usage at
- All configuration needs to be done over the console/terminal.
- Already existing clients needs to be checked and possibly reconfigured if related directives are set.
- The OpenVPN server needs to be stopped, the configuration be saved (press the save button) and then be started again after the local configuration files were modified to write all made changes to the main configs.
- fragment — Fragments the unencrypted UDP packets to be sent through the tunnel to the maximum byte size of the package. The UDP header is not included. This option works only with UDP tunnels. To deactivate «fragment» the value of the field have to be empty.
- mssfix — Used for TCP packets that are sent via a UDP tunnel. The TCP connection is handed over , the maximum packet size in bytes. Unless no other value is edited in the configuration file, mssfix uses the same value than fragment.
| Note! |
|---|
| 1) To adapt «mssfix» and «fragment» for your own specific infrastructure, it also can be helpful to perform an . |
| 2) «mssfix» and «fragment» should only be used with the UDP protocol, TCP should be regulated by the MTU size only. |
- Max-Clients — Limits the number of clients with parallel connections (default 100)
- Keepalive — Used to control the tunnel and keep it with ping and ping-restart alive.
Untangle
Untangle NG Firewall takes the complexity out of network security—saving users’ time. This firewall is intended to balance performance and protection, policy and productivity. It’s an ideal fit for a range of organisations seeking a powerful, cost-effective network security solution that can handle any IT challenge — from small, remote offices to diverse school campuses and large, distributed organisations. The NG Firewall has different software modules that can be enabled or disabled as per individual requirements. These software modules are also called apps. They are both free and paid apps. So, for full functionality, you have to buy subscriptions for what you want.
Features
- Virus blocker
- Firewall
- Web monitor
- Spam Blocker Lite
- Ad blocker
- OpenVPN
- Captive portal
- Intrusion prevention
- Phish blocker
According to me, these are the best firewalls available in the open source world. I have chosen them as they are cost-effective and user friendly. Others may have a different opinion.
logfile options
-
Verb — Defines the debug level. Range of values:
- The value scale goes from 0 to 11. Hereby different processes of the OpenVPN connection are minuted and can be used for debugging or optimization.
- Range of values: The value scale goes from 0 to 11. There will be different sequences of the OpenVPN connection Logged and can be used for debugging or optimization. The default value is set at level 3 which delivers a good overview over the connection (interface, routing, encryption, etc.).
| Note! |
|---|
| With a verbose Mode of 6 a normal usage of the server is not properly possible. Modes 6 and more are intended for debugging purposes. |
Настройка
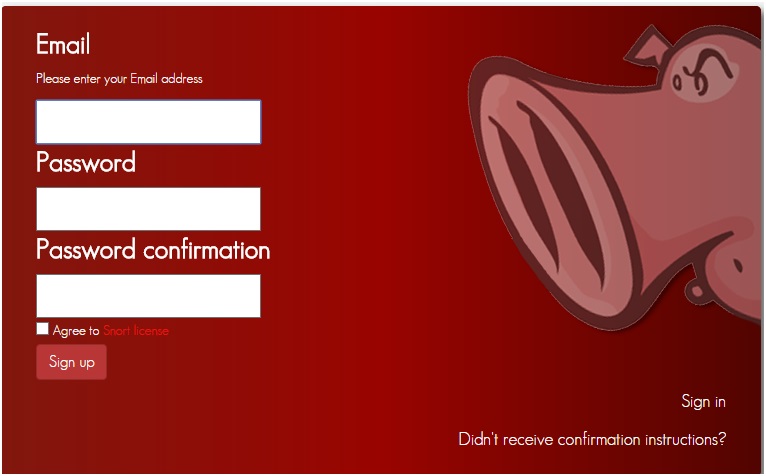

Получив Oinkcode вводим его в веб интерфейсе IPFire. Services-Intrusion Detection System. Вводим в бокс Oinkcode.
DHCP
DHCP в локальной сети
Во вкладке Network / DHCP configuration можно настроить конфигурации для DHCP в локальной сети. (Зеленый интерфейс)

В указанном примере диапазон выдаваемых IP от Start address-10.0.0.11 до End Address-10.0.0.20. Но максимальный диапазон , который можно установить согласно маске 2^8=256.
DMZ
DMZ можно задать во время установки МЭ. Настроить ее можно путем создания нескольких rule.
- Откройте “Firewall” > “Firewall Rules”
- Destination укажите Standard network и выберете ORANGE
- В протоколах можно оставить All
- Выберем drop снизу и добавляем описание
Создаем еще несколько правил уже c такими же настройками кроме как в протоколе выберем TCP укажем порт 80 и выбираем вместо drop accept. То же самое выполним для порта 22. Не забудем убедиться что rule position у 2х последних под приоритетом чем у 1 го созданного нами rule.
DNS
Настройка DNS. Сперва, создать IPFire Service Group для DNS
- В IPFire WUI(Веб интерфейс), открыть Firewall > Firewall Groups
- Нажать кнопку “Service Groups”
- В боксе Group Name: введите ‘DNS’
- Нажмите Add
- Нажмите желтый карандаш рядом с DNS service group для редактирования
- Во вкладке Add выберите DNS (TCP) и нажмите Add
- В боксе Add выберете DNS (UDP) и нажмите Add
Затем, настройте новые firewall rules
- Откройте Firewall > Firewall Rules
- Нажмите кнопку Apply changes, так как для создания нового DNS Service Group
- Нажмите кнопку New rule и настройте следующие строки:
- Source: Standard networks GREEN
- Проверьте Use Network Address Translation (NAT) и оставьте Firewall Interface в режиме — Automatic —
- Firewall: GREEN
- Protocol: — Preset —
- Service Groups DNS
- Добавьте комментарий к строке Remark:, например Предотвращает DNS hijacking attack — GREEN
- Нажмите кнопку Add
- Вернемся во вкладку Firewall Rules, нажмите кнопку Apply changes сверху
- Создайте еще 1 идентичный rule, но для каждой отдельной сети что у вас есть, например за синих:
- Нажмите кнопку New rule и настройте следующие строки:
- Source: Standard networks BLUE
- Проверьте Use Network Address Translation (NAT) и оставьте Firewall Interface в режиме — Automatic —
- Firewall: BLUE
- Protocol: — Preset —
- Service Groups DNS
- В бокс Remark: добавьте комментарий, like Prevent DNS hijacking attack — BLUE
- Нажмите кнопку Add
Вернувшись в Firewall Rules нажмите Apply changes сверху.
Блокировать доступ к mail.ru можно создать фильтр. Откройте вкладку URL filter в подразделе network. В бокс Custom blacklist добавьте www.mail.ru .Поставьте галку Enable custom blacklist.
Логирование
Уметь отслеживать SSH, HTTP, HTTPS и DNS запросы в сети
Чтобы отслеживать подобные запросы достаточно добавить несколько новых rule.
Протокол TCP справа указываем порты 53(DNS) , 443(HTTPS),22(SSH), 80(HTTP). И еще Протокол UDP порт 53 (DNS). Выбираем Accept в каждом, но в rule position ставим низкий приоритет, так чтобы мы могли ловить логи, но не повлияем на другие правила.
Roadwarrior connection (Host-to-Net)
So-called «Roadwarrior» connections are those connections that are generally made from a client PC back to the firewall to establish a connection to the Green/Blue networks, or to access the internet through an encrypted tunnel. This is frequently done with OpenVPN, but using IPSec has the major advantage of not requiring the user to install a VPN client on their computer.

Example Configuration — Roadwarrior with WindowsExample Configuration — Roadwarrior with MacOSExample Configuration — Roadwarrior with AndroidExample Configuration — Roadwarrior with Windows Phone 8.1
FIXME Instructions for Roadwarrior connections with Linux systems are missing at the moment.
Конфигурация
После перезагрузки будет выполнена базовая конфигурация брандмауэра IPfire. Прежде всего, выбраны раскладка клавиатуры и часовой пояс.
Имя хоста и локальный домен для брандмауэра IPfire.
Настройка пароля для пользователя root, который используется для доступа CLI для IPfire.
Настройка пароля для пользователя admin, который используется для доступа в сеть IPfire.
Ниже приведена конфигурация сети IPfire. Как показано на рисунке, конфигурация сети по умолчанию — ЗЕЛЕНЫЕ и КРАСНЫЕ. Однако он также поддерживает зоны BLUE и ORANGE.
Зоны, поддерживаемые IPfire, показаны на следующем рисунке.
В стандартной установке межсетевого экрана IPfire, Зелёная + Торт означает 2 Networks. Зелёная сеть для дома или локальной сети и Торт сеть для интернет / внешнего подключения.
Использование каждой зоны приведено в следующей таблице.
Назначение доступных сетевых карт в ЗЕЛЕНУЮ и КРАСНУЮ зону показано в следующих моментальных снимках.
Интерфейсы, назначенные как ЗЕЛЕНЫМ, так и КРАСНЫМ зонам, показаны на рисунке ниже.
Настройка IP-адреса для ЗЕЛЕНЫХ зон показана ниже.
Назначенный IP-адрес и сетевая маска соответствуют IP = 192.168.1.115, Net mask = 255.255.255.0
Настройка IP-адреса для RED-зоны показана ниже.
Назначенный статический IP-адрес и сетевая маска следующие. Однако режимы DHCP и PPP DIALUP (PPPoE) также поддерживаются на RED-интерфейсе для назначения IP-адресов.
IP = 192.168.100.1, маску сети = 255.255.255.0
Настройка DNS и шлюза для RED-интерфейса показана в следующем снимок.
Конфигурация DHCP на интерфейсе GREEN для автоматического назначения IP приведена ниже.
После настройки DHCP базовые настройки IPfire завершены.
IPfire перезагрузится, чтобы применить изменения и предоставит CLI доступ пользователю «root».
Для доступа к CLI введите пароль для пользователя «root».
Для дальнейшей настройки требуется веб-доступ IPfire. Он также используется для настройки правил брандмауэра, настройки snort и настройки VPN и т. Д.
Введите IP-адрес GREEN интерфейса по порту 444 для доступа к веб-интерфейсу. Все веб-браузеры предоставляют исключение из-за ненадежных сертификатов. Поэтому принимайте исключение для просмотра веб-страниц.
Введите пароль для пользователя «admin» для доступа к страницам.
После правильного имени пользователя и пароля появляется следующая основная панель, в которой отображается сетевая конфигурация (IP-адреса в зонах RED и GREEN).
VyOS
VyOS is an open source network operating system based on Linux and includes multiple applications such as Quagga, ISC DHCPD, OpenVPN, StrongS/WAN and others, under a single management interface. It can be installed on any physical hardware, on a virtual machine or a cloud platform.
Features
- VLANs
- Static and dynamic routing
- Firewall rulesets for IPv4 and IPv6 traffic
- Tunnel interfaces
- PPPoE, GRE, IPIP, SIT, static L2TPv3, VXLAN
- VPN
- NAT
- DHCP and DHCPv6 server and relay
- NetFlow and sFlow
- Web proxy and URL filtering
- QoS policies (drop tail, fair queue, and others), traffic redirection
- VRRP, connection table synchronisation
Introduction
The examples on this page assume that your IPFire devices are connected directly to the internet. If you have some sort of NAT router between you and the public internet, you should first eliminate that router by removing it or by setting it into «Bridge» mode.
Additionally, we assume that you have either a static IP for your Red interface, or if you do not, we assume that you have an automatically updated dynamic DNS hostname. Dynamic DNS hostnames are configured in the WebGUI underServices / Dynamic DNS, see Dynamic DNS. Make sure, that the static IP address / dynamic DNS name is reachable from the other IPFire, e.g. ping from IPFire1 the remote IP address / dynamic DNS name of IPFire2 and ping from IPFire2 the remote IP address / dynamic DNS name of IPFire1.
While you can use a dynamic IP address without a dynamically updated hostname, you will have to modify your settings each and every time that your address changes.
Virtual Private Networks (VPN) using IPSec can be defined as a Host-to-Net VPN (RoadWarrior) or a Net-to-Net VPN. Both types of configuration are described below.
System Details
The project is regularly updated by the development team to maintain the security. Developed as a stateful packet inspection (SPI) firewall.
IPFire separates the network into different segments based on their security risk which are organised in colours. Normal clients connected to the LAN are represented as green, the Internet is represented as red, an optional DMZ is represented as orange and an optional Wireless network is represented as blue. No traffic can flow between segments unless specifically permitted through a firewall rule .
IPFire’s package management system, called Pakfire allows to install system updates, which keep security up to date, and additional software packages for customisation to different usage scenarios and needs. The Linux system is customised for the concrete purpose of a firewall.
The design is modular, making its functionalities extensible through plugins, but the base comes with the following features
- Stateful packet-inspection firewall based on Linux Netfilter
- Proxy server with content filter and catching-updates functions (e.g. Microsoft Windows updates, virus scanners, etc.)
- Intrusion detection system (Snort) with the option to install the Intrustion Prevention System guardian via Pakfire
- Since Core Update 131 it features the intrusion prevention system «Suricata» instead of snort
- Virtual private network (VPN) with IPsec and OpenVPN
- Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol (DHCP) server
- Caching name-server (supports DNSSEC )
- Time server
- Wake-on-LAN (WOL)
- Dynamic DNS
- Quality of service (QoS)
- System monitoring functions and log analysis
- GeoIP filtering
- Captive Portal
Меню IPFire
Это меню используется для базовых настроек машины IPFire, таких как включение доступа ssh, резервное копирование и установка пароля веб-доступа и т. Д. Системное подменю показано на следующем рисунке.
В этом меню администратор брандмауэра рассматривает состояние системных ресурсов, таких как оперативная память и процессор, внутренняя и внешняя сеть, энтропия для TRNG и статистика для VPN.
Как показано на следующем рисунке, в этом меню доступны сетевые настройки, такие как статическая маршрутизация, веб-прокси, фильтрация URL-адресов и пробуждение по Lan и т. Д.
В этом меню перечислены такие службы, как VPN, которые включают IPsec и OpenVPN, обнаружение вторжений, QoS, сервер времени и т. Д.
брандмауэр
Основной функцией распространения IPFire является функция брандмауэра. Администратор или пользователь использует это меню для ввода правил iptables на задней панели.
Pakfire используется для установки дополнений / пакетов на машине IPFire для получения дополнительной функции.
Как показано на следующем рисунке, журналы журналов служб, таких как IDS, брандмауэр, прокси и система могут быть просмотрены в меню Журналы.
В этой статье мы сосредоточили внимание на установке и настройке другого брандмауэра с открытым исходным кодом, IPFire. Он разветвлен от известных брандмауэров с открытым исходным кодом IPCop и Endian
Он обеспечивает высокую доступность, использование функций TRNG и AES-NI.
Setting up the Blue Network
Initial Setup
If the blue network has not been created and linked to an actual wireless card you will have to do that first. This can be done during installation but can also be done in the console later on.
To setup the blue network from the console, login as «root» using your password. Then type:
setup
and navigate to «Network configuration».
Here you will need to modify «Network configuration type», «Drivers and card assignments» and «Address settings».
The Network configuration type must be one of the two types with a blue network.
Important — It is important to give the blue network a different subnet than the other zones.
- Having defined a new blue network a compatible wireless card must be assigned to it in «Drivers and card assignments».
- «Address settings» will be covered in the next section.
Addressing
Important — IPfire treats the Blue network as a completely separate network. By default clients cannot connect with the Green network from it. If a client on the Blue network needs to communicate with a device on the Green network you must add a rule to the firewall allowing access. Alternatively you can bridge the two networks with Zone Configuration but this adds some security risk.
The blue interface needs a static IP address out of the blue network assigned to it. Make sure the green and blue are distinct.
For example if you have the green network setup using the 192.168.0.0/24 subnet, use the 192.168.1.0/24 subnet for the blue network.
Once a suitable IP address has been determined it should be assigned in the console under «Address settings».
It is common use, to choose the first or last client address in the subnet ( i.e. .1 or .254 in a /24 net ).
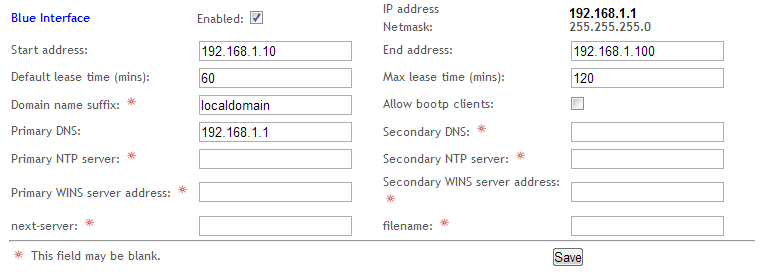
DHCP
Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol is needed to pass out IP address to connecting clients. Chose a range of IP addresses that is from the same subnet as the blue network’s default gateway address. The range cannot include the default gateways address. This range can then be set in the console or in the WUI under «network>DHCP server».
Shell tools
Tools for the IPFire Console or to use through a SSH connection
Network tools
- bwm-ng is a bandwidth monitor
- fping works like ping, but can be used for scanning entire networks
- HAProxy
- Iftop is a realtime bandwidth monitor
- IPerf/JPerf allows you to test your network speed (LAN or WLAN)
- iptraf-ng is a console-based network statistic monitoring utility
- keepalived can be used for virtual services and 1st hop redundancy (VRRP)
- mtr combines the functions of trace-route and ping in one tool
- nmap is a versatile (and powerful) IP/port scanner
- nginx is an HTTP and reverse proxy server, as well as a mail proxy server
- stunnel — A SSL encryption wrapper
- tcpdump is a tool to watch and control your network connections
- traceroute is a network tool used to follow your packets through the internet
- tshark is a network protocol analyzer and the terminal oriented version of wireshark
- netcat is a network tool for reading and writing to network connections using TCP/UDP
- avahi is a system which facilitates service discovery via the mDNS/DNS-SD protocol suite
- dehydrated is a client for signing certificates with a Let’s Encrypt server
- frr (FRRouting) is an IP routing protocol suite
- bird is an Internet Routing Daemon with support of all modern routing protocols
- speedtest-cli is a command line interface for testing Internet bandwidth
Other tools
Tools to be used on the IPFire Console or through a Secure Shell connection
- htop is a process viewer similar to «top» but with many more features
- igmpproxy is a simple multicast routing daemon based on mrouted
- LCD4Linux grabs information and displays it on an external liquid crystal display
- mc the good old Midnight Commander; an easy to use file manager
- nano is a text editor, much easier to use than VI
- Net-SNMP daemon is a SNMP implementation and more advanced than the basic snmpd
- rsync is a file copying and backup utility
- Tmux is a terminal multiplexer for the console
- 7zip is a file archiver with a high compression ratio
- ghostscript is a Postscript interpreter, PDF interpreter and rendering engine
- joe is a full featured terminal-based screen editor
- minicom is a text-based modem control and terminal emulation program for serial communications
- telnet is used for interactive communicate with another host using the TELNET protocol
- powertop is a tool to diagnose issues with power consumption and power management
- ddrescue is a data recovery tool
- wavemon is a wireless network monitor
- sysbench is a system evaluation benchmark
- flashrom is a utility to detect, read, write, verify and erase flash chips
Version 15.1 Highlights
Debian 10 Update
This release updates NG Firewall’s operating system to the current stable release of Debian, called Debian 10 (code name Debian Buster).
As with all operating systems, continued improvements are needed to maintain proper security, compatibility and functionality as technology advances. Being on the latest version of Debian ensures that all bugs, enhancements and any vulnerabilities discovered in previous releases of Debian are addressed. Debian 10 also provides driver support for additional and new network devices, including those based on Intel X553 chipsets.
For a full list of changes in NG Firewall 15.1, please see the changelog.
Pricing and Availability
Untangle NG Firewall version 15.1 is available as a free download. Current Untangle customers will be able to upgrade seamlessly at no charge.
Important Technical Notes
This release includes a Debian Linux kernel update to version 4.19.0-4 that will require a reboot and will reindex the database.
Because upgrading to NG Firewall 15.1 requires a reboot and reindexing of the database, consideration should be made on the timing for the upgrade to ensure it is done at a time when it is acceptable. For deployments with large database repositories, reindexing could take over an hour. While the database is reindexing, the appliance is online and working, but the dashboard will not be updating. Visit the Upgrade Settings page in our documentation for more information.
Security
The whole point of IPsec (or any other VPN solution) is to secure your communications and ensure that any traffic you send has not been modified while in transit. If you are not careful, it is possible to create a VPN tunnel that is not sufficiently secure to properly safeguard your data.
To this end, it is imperative that you spend some time learning about what you need to do to properly set up an IPsec tunnel. Reading the Strongswan Security Recommendations is a good place to start. While this information is geared to IPSec tunnel implementations, it is just as important to proceed carefully when creating other types of VPN tunnels.
Advanced Settings and Cipher Selection
Some of the encryption schemes supported by IPSec are widely considered insecure, but are included for backwards compatibility with older devices that are still common. MODP-1024, MODP-1536, SHA1, and MD5 are all examples of insecure ciphers that should generally be avoided unless you absolutely MUST use them.
You can select which encryption methods will be used by a tunnel on the advanced settings page, but that is not enough, as Strongswan (the software implementing IPSec on IPFire) will, by default, use any compatible encryption scheme if the other side initiates the connection. The way to avoid this is to enable the «IKE+ESP: Use only proposed settings» checkbox, which will ensure that only those ciphers you select on the advanced settings page will be used.
You may prefer to leave this checkbox disabled until you have successfully established a tunnel. Then, once you know it is working, you can enable it and confirm that doing so does not cause a problem. If selecting the «IKE+ESP: Use only proposed settings» checkbox does prevent you from successfully establishing a tunnel, then the methods you have selected are not supported by the remote device, and you will need to select different settings that are supported by the remote device.
Net to Net:
When setting up a tunnel that will always be connecting the same two devices, it is a good idea to choose a single combination of ciphers on both sides. Selecting multiple options in the various areas serves no purpose.
Road Warrior
When setting up a Road Warrior tunnel, you should limit the available ciphers to those supported by the devices that you know will be connecting to your server. It will likely make sense to select multiple choices in each selection box to ensure that different devices supporting different schemes will all work.

On-Demand
In this mode, the VPN connection will be established when needed. If it is not needed any more, it will be shut down after 15 minutes of inactivity. This helps to save resources on not very frequently used VPNs.
pfSense
pfSense is an open source security solution with a custom kernel based on the FreeBSD OS. It is a software distribution that is customised especially to be used as a firewall and router. This open source firewall can be installed on bare metal hardware and be managed entirely through a Web interface. Apart from firewalling and routing platforms, you can expand its functionality by using its many features, without adding bloat and potential security vulnerabilities to the base distribution.
Features
- Firewall – IP/port filtering, limiting connections, Layer 2 capable, scrubbing
- State table – By default, all rules are stateful, and there are multiple configurations available for state handling
- Server load balancing (LB) – Inbuilt LB to distribute load between multiple backend servers
- NAT (network address translation) – Port forwarding, reflection
- HA (high-availability) – Failover to secondary if primary fails
- Multi-WAN (wide area network) – Uses more than one Internet connection
- VPN (virtual private network) – Supports IPsec and OpenVPN
- Reporting – Keeps historical resource utilisation information
- Monitoring – Real-time monitoring
- Dynamic DNS – Multiple DNS clients are included
- DHCP and relay ready
Some examples:
- Security – Stunner, Snort, Tinc, Nmap, arpwatch
- Monitoring – iftop, ntopng, Softflowd, urlsnarf, darkstat, mailreport
- Networking – NetIO, nut, Avahi
- Routing – FRR, OLSRd, routed, OpenBGPD
- Services – Iperf, widentd, syslog-ng, bind, Acme, Imspector, Git, DNS-server
#7 IPCop (https://distrowatch.com/)
IPCop is a Linux-based OS that helps secure your home or company’s network. It does not include a graphical interface. It is operated entirely by command line, which may make it difficult for some users to install and set up.
While the software may require technical knowledge of servers and firewalls, it provides a lightweight option for more advanced users. The image size is just 60MB and designed for i486 architecture systems.
Unfortunately, the software is no longer supported. The last update was released in 2012. However, the software is still available for download through several distribution archive websites.
#4 ClearOS (https://www.clearos.com/)
ClearOS is a Linux-based firewall designed for installation on Linux servers. It provides a solution for monitoring and controlling access to local services and applications of the machine as well as the rest of the network. Thus, it’s a local software firewall that protects the server on which it is installed but also it can act as network firewall as well.

The base features of ClearOS are easy to set up and provide a simplified option for adding an extra firewall. It is a lightweight program with a web-based interface. However, the developers also have a custom firewall tool that can be used to add IPTABLES rules to the machine therefore protecting more complex network environments.
For advanced users, there is an advanced firewall tool. Users can use this tool to establish special firewall rules or allow connections to webconfig.
LAN Cards/Onboard Chips
| LAN-Card name | Type | ID | Loaded Modules/Drivers | tested with Core | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Attansic/Atheros | |||||
| Attansic Technology Corp. L2 100 Mbit Ethernet Adapter (rev a0) | 100 MBit/s | 1969:2048 | atl2 | 100 | |
| AR8131 Gigabit Ethernet (rev c0) | 1000 MBit/s | 1969:1063 | atl1c | 66 | |
| Broadcom Corporation | |||||
| NetXtreme BCM5723 Gigabit Ethernet PCIe (rev 10) | 1000 MBit/s | 14e4:165b | tg3 | 100 | |
| D-Link Corp. | |||||
| DFE-538TX 10/100 Ethernet Adapter (rev 10) | 100 MBit/s | 1186:1300 | 8139too | 66 | |
| Intel Corporation | |||||
| Intel 82557/8/9/0/1 Ethernet Pro 100 (rev 08) | 100 MBit/s | 8086:1229 | e100 | 66 | |
| Intel 82566DC Gigabit Network (rev 02) | 1000 MBit/s | 8086:104b | e1000e | 72+ | Built in to OEM motherboard |
| Intel 82566DM-2 Gigabit Ethernet Connection (rev 02) | 1000 MBit/s | 8086:10bd | e1000e | 66 | |
| Intel 82574L «Gigabit CT Desktop Adapter» (PCIe) | 1000 MBit/s | 8086:10d3 | e1000e | 66,72-74 | |
| Intel Corporation I350 Gigabit Network Connection (rev 01) | 1000 MBit/s | 8086:1521 | igb and igbvf | 75-101 | Built into Intel motherboard. Tested in virtual machine using KVM, works with both pci passthrough of physical function, and with virtual function using SR-IOV |
| Intel Corporation I211 Gigabit Network Connection (rev 03) | 1000 MBit/s | 8086:1539 | igb | 119-123 | |
| NVidia Corporation | |||||
| MCP73 Ethernet (rev a2) | 1000 MBit/s | 10de:07dc | forcedeth | 100 | |
| Realtek Semiconductor Co., Ltd. | |||||
| RTL8101E/RTL8102E PCIe Fast Ethernet (rev 02) | 100 MBit/s | 10ec:8136 | r8101 | 100 | |
| RTL8139/8139C/8139C+ Fast Ethernet (rev 02) | 100 MBit/s | 10ec:8139 | r8139too | 66 | |
| RTL8152 Gigabyte Ethernet | 1000 MBit/s | r8152 | 142 | example in nano pi R1 | |
| RTL8111/8168B PCIe Gigabyte Ethernet (rev 03) | 1000 MBit/s | 10ec:8168 | r8168 | 100 | |
| RTL8111/8168E PCIe Gigabyte Ethernet (rev 06) | 1000 MBit/s | 10ec:8168 | r8169 | 117 | |
| RTL8110SC/8169SC Gigabyte Ethernet (rev 10) | 1000 MBit/s | 10ec:8169 | r8169 | 100 | |
| RTL-8029(AS) | 10 MBit/s | 10ec:8029 | ne2k-pci | 66 | |
| Super Micro Computer, Inc. | |||||
| AOC-SGP-I2 Supermicro PCI-e 2-port Intel i350 Gigabit Ethernet LAN card | 1000 MBit/s | 8086:1521 | igb and igbvf | 75-101 | PCI-Express card. Tested in virtual machine using KVM, works with both pci passthrough of physical function, and with virtual function using SR-IOV |
| VIA Technologies, Inc. | |||||
| VT6102 Embedded Ethernet Controller on VT8235 | 100 MBit/s | 1106:0102 | via_rhine | 66-85 | onboard Mercury PVCLE266M-L V3.0A mainboard, mainboard now incompatible with GRUB2 |
#8 ufw (https://help.ubuntu.com/community/UFW)
UFW is a configurable firewall designed for the Ubuntu Linux operating system. Uncomplicated Firewall (UFW) is the default configuration tool for Ubuntu. However, it is disabled by default.
When users turn on the UFW program, all incoming traffic is denied, other than a few exceptions that are included to make setup easier for home users.
Users can then choose to allow or deny traffic to suit their needs. You can quickly add or delete rules through the Linux terminal. For home users, a GNU frontend is available for download that provides a desktop graphical interface. However, most of its configuration in done using CLI commands.
This is a local firewall for protecting only the server it is installed on.
NG Firewall Apps
Untangle NG Firewall is a platform which includes a growing ecosystem of technology applications, or ‘apps’. This ‘app’ approach to features and functionality make Untangle NG Firewall exceptionally easy to use by greatly simplifying the UI, and tailoring it for each deployment.
Proactively block malware, phishing, spam, hacking and other exploits from reaching users and devices on the network.
Ensure network performance and bandwidth for your organization’s business-critical cloud apps. Maximize uptime and QoS to increase productivity and minimize recreational traffic.
Get a handle on every rogue application, encrypted web request, malware distribution point and rash of spam.
Maintain visibility and control over remote workers, branch offices and guest Wi-Fi. Keep users and data safe, no matter their location or level of access.
Create policies by user, group, device, time and more to control who can access websites, data or apps. Get complete visibility into and control over network traffic.
Get expert help from our tech support team. Rebrand NG Firewall to reflect your brand in the administrative interface and on block pages.
Check out our Current Release page for more information about the latest version of Untangle, including point releases.
IPFire
IPFire is built on top of Netfilter and is an open source distribution. IPFire was designed with both modularity and a high level of flexibility in mind. It can be used as a firewall, proxy server or VPN gateway. The IDS (intrusion detection system) is inbuilt, so attacks are detected and prevented from Day One. And with the help of Guardian (an optional add-on), you can implement automatic prevention.
Features
- Stateful packet inspection (SPI)
- Proxy server with content filter and caching functionality
- Intrusion detection system
- VPN via IPsec and OpenVPN
- DHCP server
- Caching name server
- Time server
- Wake-on-LAN (WOL)
- Dynamic DNS