Vba isnumeric
Содержание:
Final Thoughts
Congratulations! You’re now an IsNumeric expert! You certainly know more about IsNumeric than the average Excel user, and for that you should be excited.
IsNumeric is a great VBA function, but, , you have to be careful when using it if there’s a chance your input may be blank or if you’re evaluating dates and times.
It’s important to know what a function does well, but it’s equally important to know what a function doesn’t do well. I hope you find this VBA tutorial informative and you’re IsNumeric in your own macros!
Oh, and if you have a question, post it in our VBA Q&A community.
The best free VBA training on the webI see people struggling with Excel every day and I want to help. That’s why I’m giving away my VBA Developer’s Kit for free to our newest subscribers.
SQL References
SQL Keywords
ADD
ADD CONSTRAINT
ALTER
ALTER COLUMN
ALTER TABLE
ALL
AND
ANY
AS
ASC
BACKUP DATABASE
BETWEEN
CASE
CHECK
COLUMN
CONSTRAINT
CREATE
CREATE DATABASE
CREATE INDEX
CREATE OR REPLACE VIEW
CREATE TABLE
CREATE PROCEDURE
CREATE UNIQUE INDEX
CREATE VIEW
DATABASE
DEFAULT
DELETE
DESC
DISTINCT
DROP
DROP COLUMN
DROP CONSTRAINT
DROP DATABASE
DROP DEFAULT
DROP INDEX
DROP TABLE
DROP VIEW
EXEC
EXISTS
FOREIGN KEY
FROM
FULL OUTER JOIN
GROUP BY
HAVING
IN
INDEX
INNER JOIN
INSERT INTO
INSERT INTO SELECT
IS NULL
IS NOT NULL
JOIN
LEFT JOIN
LIKE
LIMIT
NOT
NOT NULL
OR
ORDER BY
OUTER JOIN
PRIMARY KEY
PROCEDURE
RIGHT JOIN
ROWNUM
SELECT
SELECT DISTINCT
SELECT INTO
SELECT TOP
SET
TABLE
TOP
TRUNCATE TABLE
UNION
UNION ALL
UNIQUE
UPDATE
VALUES
VIEW
WHERE
MySQL Functions
String Functions
ASCII
CHAR_LENGTH
CHARACTER_LENGTH
CONCAT
CONCAT_WS
FIELD
FIND_IN_SET
FORMAT
INSERT
INSTR
LCASE
LEFT
LENGTH
LOCATE
LOWER
LPAD
LTRIM
MID
POSITION
REPEAT
REPLACE
REVERSE
RIGHT
RPAD
RTRIM
SPACE
STRCMP
SUBSTR
SUBSTRING
SUBSTRING_INDEX
TRIM
UCASE
UPPER
Numeric Functions
ABS
ACOS
ASIN
ATAN
ATAN2
AVG
CEIL
CEILING
COS
COT
COUNT
DEGREES
DIV
EXP
FLOOR
GREATEST
LEAST
LN
LOG
LOG10
LOG2
MAX
MIN
MOD
PI
POW
POWER
RADIANS
RAND
ROUND
SIGN
SIN
SQRT
SUM
TAN
TRUNCATE
Date Functions
ADDDATE
ADDTIME
CURDATE
CURRENT_DATE
CURRENT_TIME
CURRENT_TIMESTAMP
CURTIME
DATE
DATEDIFF
DATE_ADD
DATE_FORMAT
DATE_SUB
DAY
DAYNAME
DAYOFMONTH
DAYOFWEEK
DAYOFYEAR
EXTRACT
FROM_DAYS
HOUR
LAST_DAY
LOCALTIME
LOCALTIMESTAMP
MAKEDATE
MAKETIME
MICROSECOND
MINUTE
MONTH
MONTHNAME
NOW
PERIOD_ADD
PERIOD_DIFF
QUARTER
SECOND
SEC_TO_TIME
STR_TO_DATE
SUBDATE
SUBTIME
SYSDATE
TIME
TIME_FORMAT
TIME_TO_SEC
TIMEDIFF
TIMESTAMP
TO_DAYS
WEEK
WEEKDAY
WEEKOFYEAR
YEAR
YEARWEEK
Advanced Functions
BIN
BINARY
CASE
CAST
COALESCE
CONNECTION_ID
CONV
CONVERT
CURRENT_USER
DATABASE
IF
IFNULL
ISNULL
LAST_INSERT_ID
NULLIF
SESSION_USER
SYSTEM_USER
USER
VERSION
SQL Server Functions
String Functions
ASCII
CHAR
CHARINDEX
CONCAT
Concat with +
CONCAT_WS
DATALENGTH
DIFFERENCE
FORMAT
LEFT
LEN
LOWER
LTRIM
NCHAR
PATINDEX
QUOTENAME
REPLACE
REPLICATE
REVERSE
RIGHT
RTRIM
SOUNDEX
SPACE
STR
STUFF
SUBSTRING
TRANSLATE
TRIM
UNICODE
UPPER
Numeric Functions
ABS
ACOS
ASIN
ATAN
ATN2
AVG
CEILING
COUNT
COS
COT
DEGREES
EXP
FLOOR
LOG
LOG10
MAX
MIN
PI
POWER
RADIANS
RAND
ROUND
SIGN
SIN
SQRT
SQUARE
SUM
TAN
Date Functions
CURRENT_TIMESTAMP
DATEADD
DATEDIFF
DATEFROMPARTS
DATENAME
DATEPART
DAY
GETDATE
GETUTCDATE
ISDATE
MONTH
SYSDATETIME
YEAR
Advanced Functions
CAST
COALESCE
CONVERT
CURRENT_USER
IIF
ISNULL
ISNUMERIC
NULLIF
SESSION_USER
SESSIONPROPERTY
SYSTEM_USER
USER_NAME
MS Access Functions
String Functions
Asc
Chr
Concat with &
CurDir
Format
InStr
InstrRev
LCase
Left
Len
LTrim
Mid
Replace
Right
RTrim
Space
Split
Str
StrComp
StrConv
StrReverse
Trim
UCase
Numeric Functions
Abs
Atn
Avg
Cos
Count
Exp
Fix
Format
Int
Max
Min
Randomize
Rnd
Round
Sgn
Sqr
Sum
Val
Date Functions
Date
DateAdd
DateDiff
DatePart
DateSerial
DateValue
Day
Format
Hour
Minute
Month
MonthName
Now
Second
Time
TimeSerial
TimeValue
Weekday
WeekdayName
Year
Other Functions
CurrentUser
Environ
IsDate
IsNull
IsNumeric
SQL Quick Ref
Создание таблицыCreate a Table
Область применения: SQL Server База данных SQL Azure Azure Synapse Analytics (Хранилище данных SQL) Parallel Data Warehouse APPLIES TO: SQL Server Azure SQL Database Azure Synapse Analytics (SQL DW) Parallel Data Warehouse
Чтобы создать таблицу, нужно указать имя таблицы, имена и типы данных для каждого столбца таблицы.To create a table, you must provide a name for the table, and the names and data types of each column in the table. Также рекомендуется указывать, допускаются ли значения NULL для каждого из столбцов.It is also a good practice to indicate whether null values are allowed in each column. Для создания таблицы необходимо иметь разрешение и разрешение для схемы, которая будет содержать таблицу.To create a table, you must have the permission, and the permission on the schema that will contain the table. Предопределенная роль базы данных имеет эти разрешения.The fixed database role has these permissions.
Большинство таблиц имеют первичный ключ, состоящий из одной или нескольких столбцов таблицы.Most tables have a primary key, made up of one or more columns of the table. Первичный ключ всегда уникален.A primary key is always unique. Компонент Компонент Database EngineDatabase Engine потребует выполнения условия неповторения значения первичного ключа в таблице.The Компонент Database EngineDatabase Engine will enforce the restriction that any primary key value cannot be repeated in the table.
Список типов данных и ссылки на их описание см. в разделе Типы данных (Transact-SQL).For a list of data types and links for a description of each, see Data Types (Transact-SQL).
Примечание
Компонент Компонент Database EngineDatabase Engine может быть установлен с учетом регистра и без учета регистра.The Компонент Database EngineDatabase Engine can be installed as case sensitive or non-case sensitive. Если компонент Компонент Database EngineDatabase Engine установлен с учетом регистра, имена объектов должны иметь одно и тоже имя.If the Компонент Database EngineDatabase Engine is installed as case sensitive, object names must always have the same case. Например, таблица с именем OrderData будет отличаться от таблицы ORDERDATA.For example, a table named OrderData is a different table from a table named ORDERDATA. Если компонент Компонент Database EngineDatabase Engine установлен без учета регистра, эти два имени таблицы будут рассматриваться как одна таблица, то есть имя может быть использовано только один раз.If the Компонент Database EngineDatabase Engine is installed as non-case sensitive, those two table names are considered to be the same table, and that name can only be used one time.
Создание таблицыCreate the table
В окне редактора запросов введите и выполните следующий код, чтобы создать таблицу .In a Query Editor window, type and execute the following code to create a table named . Столбцы таблицы имеют имена , , и .The columns in the table are named , , , and . Столбец является первичным ключом таблицы.The column is the primary key of the table. , , и ., , , and are all data types. Только столбцы и могут быть пустыми при вставке или изменении строки.Only the and columns can have no data when a row is inserted or changed. Данная инструкция содержит необязательный элемент (), называемый схемой.This statement contains an optional element () called a schema. Схема — это объект базы данных, к которому принадлежит таблица.The schema is the database object that owns the table. Если вы являетесь администратором, схемой по умолчанию будет схема .If you are an administrator, is the default schema. означает владельца базы данных. stands for database owner.
Number Type Conversion
Python converts numbers internally in an expression containing mixed types to a common type for evaluation. But sometimes, you need to coerce a number explicitly from one type to another to satisfy the requirements of an operator or function parameter.
-
Type int(x) to convert x to a plain integer.
-
Type long(x) to convert x to a long integer.
-
Type float(x) to convert x to a floating-point number.
-
Type complex(x) to convert x to a complex number with real part x and imaginary part zero.
-
Type complex(x, y) to convert x and y to a complex number with real part x and imaginary part y. x and y are numeric expressions
Python NumPy
NumPy IntroNumPy Getting StartedNumPy Creating ArraysNumPy Array IndexingNumPy Array SlicingNumPy Data TypesNumPy Copy vs ViewNumPy Array ShapeNumPy Array ReshapeNumPy Array IteratingNumPy Array JoinNumPy Array SplitNumPy Array SearchNumPy Array SortNumPy Array FilterNumPy Random
Random Intro
Data Distribution
Random Permutation
Seaborn Module
Normal Distribution
Binomial Distribution
Poisson Distribution
Uniform Distribution
Logistic Distribution
Multinomial Distribution
Exponential Distribution
Chi Square Distribution
Rayleigh Distribution
Pareto Distribution
Zipf Distribution
NumPy ufunc
ufunc Intro
ufunc Create Function
ufunc Simple Arithmetic
ufunc Rounding Decimals
ufunc Logs
ufunc Summations
ufunc Products
ufunc Differences
ufunc Finding LCM
ufunc Finding GCD
ufunc Trigonometric
ufunc Hyperbolic
ufunc Set Operations
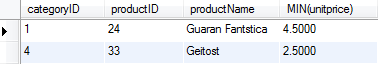
IsNumeric vs ISNUMBER
To test how the IsNumeric VBA and the ISNUMBER Excel functions behave, we’re going to make a User Defined Function (UDF) to evaluate the following cells in Column A:
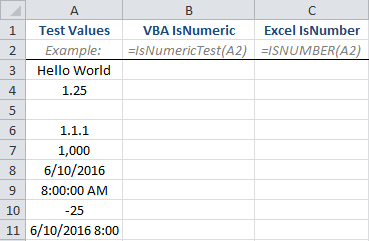
We’ll use the native ISNUMBER function of Excel in Column C and we’ll use the the following UDF to represent our VBA IsNumeric function in Column B.
We’ll evalulate the expressions in Column A using both the VBA function (Column B) and the Excel function (Column C). You would expect them to be identical, right? You’re about to be surprised…
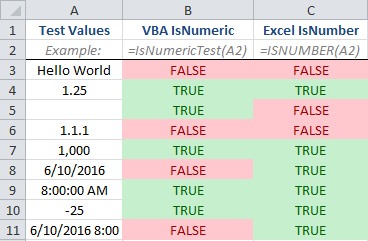
The two functions yield completely different answers when evaluating the same data. IT’S CRAZY!
By looking at the comparison image, you can see the VBA IsNumeric function considers empty cells numeric, but the Excel ISNUMBER function does not. That’s why I said earlier that it’s a good VBA practice to check if your cell is empty by using the function when you use the IsNumeric function.
Another difference you can see is in how the two functions treat dates and times. IsNumeric VBA says times are numbers, but dates are not. It also says the combination of dates and times are not numeric. ISNUMBER, on the other hand, says all 3 date/time cells are numeric.
Random Number Functions
Random numbers are used for games, simulations, testing, security, and privacy applications. Python includes following functions that are commonly used.
| Sr.No. | Function & Description |
|---|---|
| 1 |
choice(seq)
A random item from a list, tuple, or string. |
| 2 |
randrange ( stop )
A randomly selected element from range(start, stop, step) |
| 3 |
random()
A random float r, such that 0 is less than or equal to r and r is less than 1 |
| 4 |
seed()
Sets the integer starting value used in generating random numbers. Call this function before calling any other random module function. Returns None. |
| 5 |
shuffle(lst)
Randomizes the items of a list in place. Returns None. |
| 6 |
uniform(x, y)
A random float r, such that x is less than or equal to r and r is less than y |
ПримерыExamples
Примеры создания последовательностей и использования функции NEXT VALUE FOR для формирования порядковых номеров см. в разделе Порядковые номера.For examples of creating sequences and using the NEXT VALUE FOR function to generate sequence numbers, see Sequence Numbers.
В большинстве из следующих примеров объекты последовательности создаются в схеме с именем Test.Most of the following examples create sequence objects in a schema named Test.
Чтобы создать схему Test, выполните следующую инструкцию.To create the Test schema, execute the following statement.
Б.B. Создание последовательности, уменьшающейся на 1Creating a sequence that decreases by 1
В следующем примере отсчет начинается с 0 и идет по отрицательным числам, уменьшаясь на единицу при каждом использовании.The following example starts at 0 and counts into negative numbers by one every time it is used.
В следующем примере создается последовательность со значениями по умолчанию.The following example creates a sequence using the default values.
Чтобы просмотреть свойства последовательности, выполните следующую инструкцию.Execute the following statement to view the properties of the sequence.
Частичный перечень выходных данных демонстрирует значения по умолчанию.A partial list of the output demonstrates the default values.
| Выходные данныеOutput | Значение по умолчаниюDefault value |
|---|---|
IsNumeric Examples
Check if a Cell is a Number
Make powerful macros with our free VBA Developer’s KitThere’s a lot to unpack here. To save time and become really good at VBA, make sure you get our free VBA Developer’s Kit below. It’s full of shortcuts, tips and pre-built macros to make writing VBA easier.
This example macro tests if the value in cell A1 is a number. If it is, the value in cell B1 says it’s a number. Otherwise, it says it’s not a number.
You don’t need to put the in the above If Statement, but I included it to make the macro easier to read.
If you have a macro that performs arithmetic expressions, it’s a good practice to use IsNumeric to make sure your input is numeric before performing the math. As a side note, it’s also a good to make sure your input isn’t empty by using the function. That’s another tutorial for another day.
Check if All Cells in a Range are Numeric
The above macro checks each cell in your range and the moment it finds one that isn’t numeric, it exits the For Each loop and lets you know there are non-numeric cells in the range.
As a programmer, you can perform different actions based on whether the entire range is numeric or not. Checks like this one give you more control over how you handle errors.
JavaScript
JS Array
concat()
constructor
copyWithin()
entries()
every()
fill()
filter()
find()
findIndex()
forEach()
from()
includes()
indexOf()
isArray()
join()
keys()
length
lastIndexOf()
map()
pop()
prototype
push()
reduce()
reduceRight()
reverse()
shift()
slice()
some()
sort()
splice()
toString()
unshift()
valueOf()
JS Boolean
constructor
prototype
toString()
valueOf()
JS Classes
constructor()
extends
static
super
JS Date
constructor
getDate()
getDay()
getFullYear()
getHours()
getMilliseconds()
getMinutes()
getMonth()
getSeconds()
getTime()
getTimezoneOffset()
getUTCDate()
getUTCDay()
getUTCFullYear()
getUTCHours()
getUTCMilliseconds()
getUTCMinutes()
getUTCMonth()
getUTCSeconds()
now()
parse()
prototype
setDate()
setFullYear()
setHours()
setMilliseconds()
setMinutes()
setMonth()
setSeconds()
setTime()
setUTCDate()
setUTCFullYear()
setUTCHours()
setUTCMilliseconds()
setUTCMinutes()
setUTCMonth()
setUTCSeconds()
toDateString()
toISOString()
toJSON()
toLocaleDateString()
toLocaleTimeString()
toLocaleString()
toString()
toTimeString()
toUTCString()
UTC()
valueOf()
JS Error
name
message
JS Global
decodeURI()
decodeURIComponent()
encodeURI()
encodeURIComponent()
escape()
eval()
Infinity
isFinite()
isNaN()
NaN
Number()
parseFloat()
parseInt()
String()
undefined
unescape()
JS JSON
parse()
stringify()
JS Math
abs()
acos()
acosh()
asin()
asinh()
atan()
atan2()
atanh()
cbrt()
ceil()
cos()
cosh()
E
exp()
floor()
LN2
LN10
log()
LOG2E
LOG10E
max()
min()
PI
pow()
random()
round()
sin()
sqrt()
SQRT1_2
SQRT2
tan()
tanh()
trunc()
JS Number
constructor
isFinite()
isInteger()
isNaN()
isSafeInteger()
MAX_VALUE
MIN_VALUE
NEGATIVE_INFINITY
NaN
POSITIVE_INFINITY
prototype
toExponential()
toFixed()
toLocaleString()
toPrecision()
toString()
valueOf()
JS OperatorsJS RegExp
constructor
compile()
exec()
g
global
i
ignoreCase
lastIndex
m
multiline
n+
n*
n?
n{X}
n{X,Y}
n{X,}
n$
^n
?=n
?!n
source
test()
toString()
(x|y)
.
\w
\W
\d
\D
\s
\S
\b
\B
\0
\n
\f
\r
\t
\v
\xxx
\xdd
\uxxxx
JS Statements
break
class
continue
debugger
do…while
for
for…in
for…of
function
if…else
return
switch
throw
try…catch
var
while
JS String
charAt()
charCodeAt()
concat()
constructor
endsWith()
fromCharCode()
includes()
indexOf()
lastIndexOf()
length
localeCompare()
match()
prototype
repeat()
replace()
search()
slice()
split()
startsWith()
substr()
substring()
toLocaleLowerCase()
toLocaleUpperCase()
toLowerCase()
toString()
toUpperCase()
trim()
valueOf()
Mathematical Functions
Python includes following functions that perform mathematical calculations.
| Sr.No. | Function & Returns ( description ) |
|---|---|
| 1 |
abs(x)
The absolute value of x: the (positive) distance between x and zero. |
| 2 |
ceil(x)
The ceiling of x: the smallest integer not less than x |
| 3 |
cmp(x, y)
-1 if x < y, 0 if x == y, or 1 if x > y |
| 4 |
exp(x)
The exponential of x: ex |
| 5 |
fabs(x)
The absolute value of x. |
| 6 |
floor(x)
The floor of x: the largest integer not greater than x |
| 7 |
log(x)
The natural logarithm of x, for x> 0 |
| 8 |
log10(x)
The base-10 logarithm of x for x> 0. |
| 9 |
max(x1, x2,…)
The largest of its arguments: the value closest to positive infinity |
| 10 |
min(x1, x2,…)
The smallest of its arguments: the value closest to negative infinity |
| 11 |
modf(x)
The fractional and integer parts of x in a two-item tuple. Both parts have the same sign as x. The integer part is returned as a float. |
| 12 |
pow(x, y)
The value of x**y. |
| 13 |
round(x )
x rounded to n digits from the decimal point. Python rounds away from zero as a tie-breaker: round(0.5) is 1.0 and round(-0.5) is -1.0. |
| 14 |
sqrt(x)
The square root of x for x > 0 |